Active Directory (AD), the backbone of most business operations, presents a particularly enticing target for cybercriminals due to its critical role in identity management. That’s why Microsoft developed a robust solution: Microsoft Defender for Identity (MDI).
In this first part of our series, we’ll explore how MDI helps safeguard organizations from identity-based threats, with insights from Orlox’s implementation expertise. Stay tuned for our next entry, which will include a hands-on tutorial detailing how to effectively use MDI within your organization.
What Is Microsoft Defender For Identity?
Active Directory (AD) is still at the heart of most businesses today. Although being extremely critical, it also offers a large attack surface for any potential attacker. This is why a lot of cyber attacks have shifted to identity-based attacks, as they offer the most bang for the buck. These attacks may lead to a security breach and cause considerable damage to any organization.
To help organizations stay aware of these advanced persistent threats, Microsoft created Microsoft Defender for Identity (MDI).
Microsoft Defender for Identity can help organizations to:
- Prevent breaches, using proactive identity security posture assessments
- Detect threats, using real-time analytics and data intelligence
- Investigate suspicious activities, using clear, actionable incident information
- Respond to attacks, using automatic response to compromised identities
Going back to the previous chapter, where we identified the Cyber attack kill chain, we can identify the following threats using Defender for Identity
| Threat | How does Defender for Identity help you? |
| Reconnaissance | Identify rogue users and attackers’ attempts to gain information. Attackers search for information about user names, users’ group membership, IP addresses assigned to devices, resources, and more, using various methods. |
| Compromised credentials | Identify attempts to compromise user credentials using brute force attacks, failed authentications, user group membership changes, and other methods. |
| Lateral movements | Detect attempts to move laterally inside the network to gain further control of sensitive users, utilizing methods such as Pass the Ticket, Pass the Hash, Overpass the Hash and more. |
| Domain dominance | View highlighted attacker behavior if domain dominance is achieved. For example, attackers might run code remotely on the domain controller, or use methods like DC Shadow, malicious domain controller replication, Golden Ticket activities, and more. |
How Does Microsoft Defender For Identity Work?
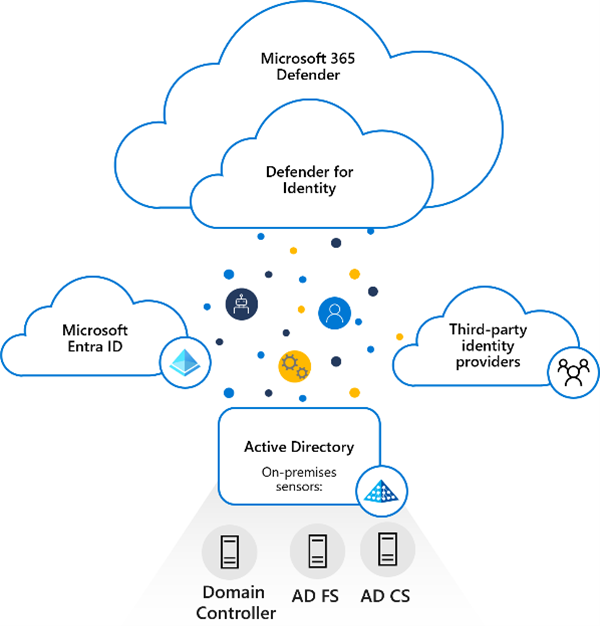
Microsoft Defender for Identity uses sensors to gather and analyze data from your Active Directory domain controllers, Azure Active Directory, and Microsoft 365 services. The sensors send the data to the cloud, where it is processed by advanced machine learning algorithms and threat intelligence. The cloud service then produces alerts and recommendations based on the detected activity and risk level.
You can see and manage the alerts and recommendations from the Microsoft Defender for Identity portal or integrate them with other security solutions such as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, Microsoft 365 Defender, or Azure Sentinel.
Defender for Identity consists of the following components:
- Microsoft Defender portal
The Microsoft Defender portal creates your Defender for Identity workspace, displays the data received from Defender for Identity sensors, and enables you to monitor, manage, and investigate threats in your network environment. - Defender for Identity sensor Defender for Identity sensors can be directly installed on the following servers:
- Domain controllers: The sensor directly monitors domain controller traffic, without the need for a dedicated server, or configuration of port mirroring.
- AD FS / AD CS: The sensor directly monitors network traffic and authentication events.
- Defender for Identity cloud service
Defender for Identity cloud service runs on Azure infrastructure and is currently hosted in the US, Europe, Australia East, and Asia. Defender for Identity cloud service is connected to Microsoft’s intelligent security graph.
Licensing Requirements
Deploying Defender for Identity requires one of the following Microsoft 365 licenses:
- Enterprise Mobility + Security E5 (EMS E5/A5)
- Microsoft 365 E5 (Microsoft E5/A5/G5)
- Microsoft 365 E5/A5/G5 Security
- A standalone Defender for Identity license
Conclusion
As we have seen, Microsoft Defender for Identity offers a comprehensive toolset designed to protect against the evolving threats targeting Active Directory and Azure Active Directory environments. As a trusted partner, Orlox is equipped to help integrate these advanced protections into your security strategy, ensuring that your identity infrastructure is both resilient and compliant.
Join us for the next installment of this series, where we will dive deeper with a practical, hands-on tutorial on setting up and optimizing Microsoft Defender for Identity. If you’re looking to enhance your organization’s security posture or require expert guidance on implementing MDI, don’t hesitate to contact Orlox today. Let us help you fortify your defenses and navigate the complex landscape of cybersecurity.



